A via is an essential component of any printed circuit board (PCB), but there are specific requirements and guidelines you should consider when selecting the right via size for your next project. Failure to do so may result in unnecessary delays and costs.
Keep reading for details on PCB via size, including the different types, standard sizes, requirements, and considerations to keep in mind when designing your next project.
What Is a PCB Via?
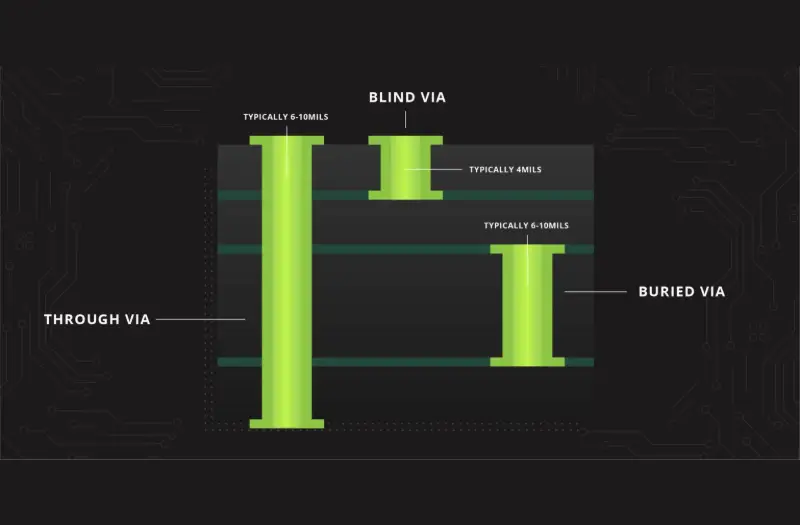
A vertical interconnect access (or via) is a plated-through hole in a printed wiring board that is used to route a trace vertically in the board from one layer to another. Through-hole vias can be drilled mechanically, and blind vias are drilled with a laser.
PCB Via Types
There are three main types of PCB vias:
- Buried via: A buried via is needed when you have what is commonly referred to as sequential lamination (or multi-lamination) projects.
- Through via-in pad: A through via connects the two exterior layers by drilling all the way through from the top to the bottom layer.
- Blind via in-pad: This via refers to a laser that only goes from one layer to the next.